July 4, 2019
Introduction
Sandalwood was once considered as the primary source of Mysore state economy where the entire budget was planned based on sandalwood.
Although India has been known for its sandalwood production for decades, it was largely confined to the forests of South Indian states and the plantations of these state governments. But, a policy change by these governments in 2002 allowed people to grow sandalwood. The Karnataka State Forest Department has liberalized the regulations related to sandalwood cultivation to ensure that there is no shortage of sandalwood in the coming future. As per the proposed amendment to the Karnataka Tree Act 1927, the forest department allows individuals to freely grow and own sandalwood trees.
Permission is given to cut a sandalwood tree in private ownership after thorough inspection by the officials. The felled tree is transported to the sandalwood depot and is auctioned after completing necessary formalities. And now, the private cultivation of this precious tree is rapidly increasing.
Key Features of Indian Sandalwood
– Indian Sandalwood is highly prized due to its aromatic fragrant wood.
– The oil extracted from sandalwood is used in perfumes, cosmetics, aromatherapy and medicinal preparations.
– Sandalwood is an extremely precious element and is used for carving.
– Indian sandalwood consists of up to 6% oil and around 90% if α and β santalols (which is claimed to be the highest).
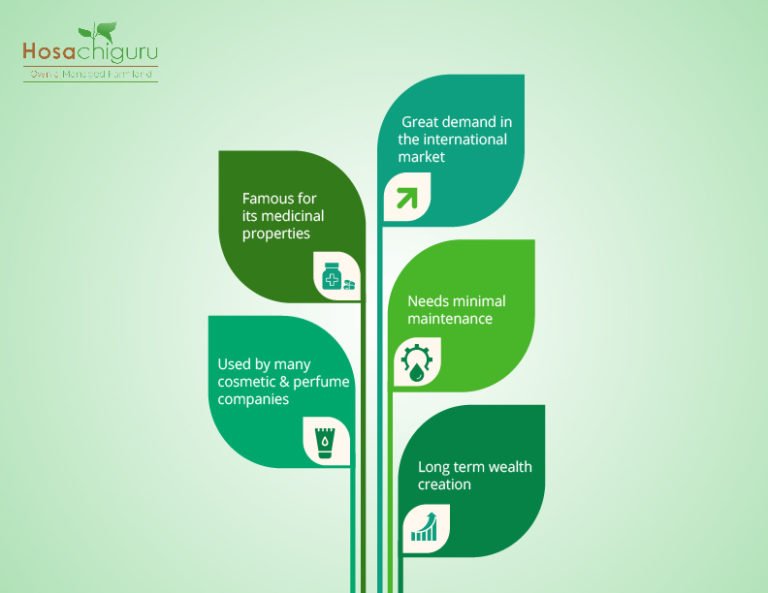
Sandalwood is in high demand (about 20,000 metric tons and oil 1000 tons) in the international markets and the current production across the world does not meet this demand which has led to a drastic rise in the sandalwood price. Sandalwood cultivation is a highly profitable business which needs very minimal maintenance. To know more about the cultivation process and maintenance details, read on…
If you are looking to invest in sandalwood cultivation, then you need the right climate, land, soil and irrigation system for the healthy growth of the trees. You must plan out the complete process in advance, in order to get high ROI (Return on Investment).
Climate Requirement
Sandalwood trees thrive well in the tropical and sub-tropical regions where the climate is hot & humid. The cultivation requires temperatures ranging from 12 degree to 40 degree Celsius and lands at reasonably higher altitudes (preferably 2000 to 3500 feet above sea level).
Soil Requirement
Sandalwood can grow in a variety of soil types including red clay soils, sandy soils and clay-rich black soils and can tolerate gravelly soil and rocky hard ground. The soil pH should range between 6 and 7.5.
Irrigation
Cultivating sandalwood plants requires less water. The young sandalwood plants need to be provided with irrigation once in 2 to 3 weeks during summer. However, they may not require irrigation in rainy conditions.
Harvesting
The sandalwood cultivation profit to an investor is tremendous and it’s the only wood in the world to be sold by weight. Its market price ranges between Rs 3,000 and Rs 7,000 per kg, with the top-quality sandalwood sometimes sold at around Rs 10,000 per kg. Once a sandalwood tree is eight years old, the heartwood of the tree starts to form and is ready to be harvested after 12 to 15 years from planting. Both in the local and international market, there is a huge demand for sandalwood. So, you are sure to get high returns from sandalwood cultivation.
From an acre of land, you can expect a yield of 5000 kg of sandalwood. The cost of sandalwood cultivation would approximately be around Rs 8 to 10 lakh per acre (https://www.agrifarming.in/sandalwood-farming-project-report-cost-profit), but the returns can range between Rs 1.5 crore to Rs 2 crore.
Accumulate fortune by investing wisely!