February 2, 2023
Author: Srinivas Abhilash
What is a Wetland?
Wetlands are areas of land that are saturated with water, either permanently or seasonally. Low-lying areas near rivers, lakes, and coastlines with the presence of hydric soils and hydrophytic vegetation (plants adapted to living in wet conditions) have swamps, marshes, bogs, fens, etc., forming a part of the wetland. In various environments, from freshwater marshes to saltwater estuaries, wetlands exist.
Wetlands in Bangalore and Real Estate
Wetlands in Bangalore, also known as “Kere” in the local language, have been at gunpoint from real estate developers for many years. The wetlands, essential for local ecology and water management, have been filled in or built on to make way for residential and commercial development. The illegal encroachment of these areas by the real estate mafia has been a central issue in the city, leading to an absence of biodiversity and environmental degradation. The government and various NGOs have been working to protect the wetlands and prosecute those involved in illegal activities, but the problem persists.
Significance of Wetlands, Role, and Importance in building a Sustainable Ecosystem
Wetlands play a vital role in maintaining the health of the environment and the well-being of human communities by providing a wide range of ecological, economic, and social benefits.
Ecological Significance:
Wetlands are incredibly rich in biodiversity and are home to a wide variety of plant and animal species, many of which are unique to these environments. They provide important habitats for migratory birds, fish, and other wildlife and are natural water filters, helping to remove pollutants and sediment from the water that flows through them. They also control floods by storing water during heavy rainfall and releasing it slowly at the appropriate time. Wetlands provide dozens of ecosystem services, such as carbon sequestration, nutrient cycling, and soil formation.
Economic Significance:
They are also a source of food and income for many people, particularly those living in rural areas. They provide room for fishing, hunting, and ecotourism and also serve as natural water resources for irrigation and domestic use.
Social Significance:
Wetlands also have significant cultural and spiritual significance for many communities. They are considered sacred places and a meaningful part of a community’s heritage. They also provide opportunities for recreation and education and can be used as an arm to promote community engagement and awareness of environmental issues.
The loss of wetlands can lead to a decline in biodiversity, increased flooding, water pollution, and detrimental to livelihoods. Hence to build a safe and healthy environment, it is essential to protect and conserve wetlands.
Why should one celebrate World Wetlands Day?
Wetlands Day is celebrated on February 2nd every year to raise awareness about the importance of wetlands and the need to protect them. Ramsar Secretariat chooses the theme of Wetlands Day every year to raise awareness of wetlands and the need to conserve them. The theme for 2022 was “Wetlands and Water” and the theme for 2023 is “Wetlands Restoration”. The purpose is to highlight the urgent need to prioritize wetland restoration.
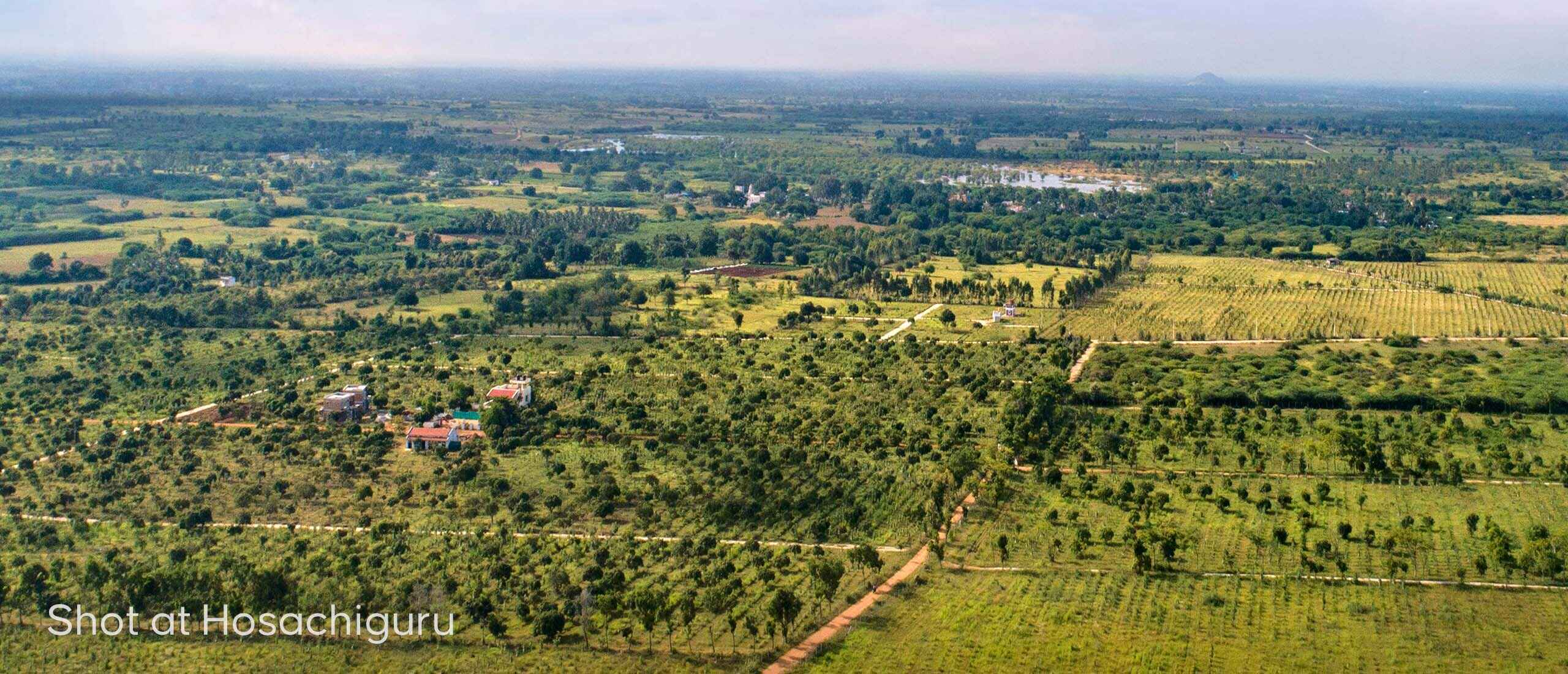
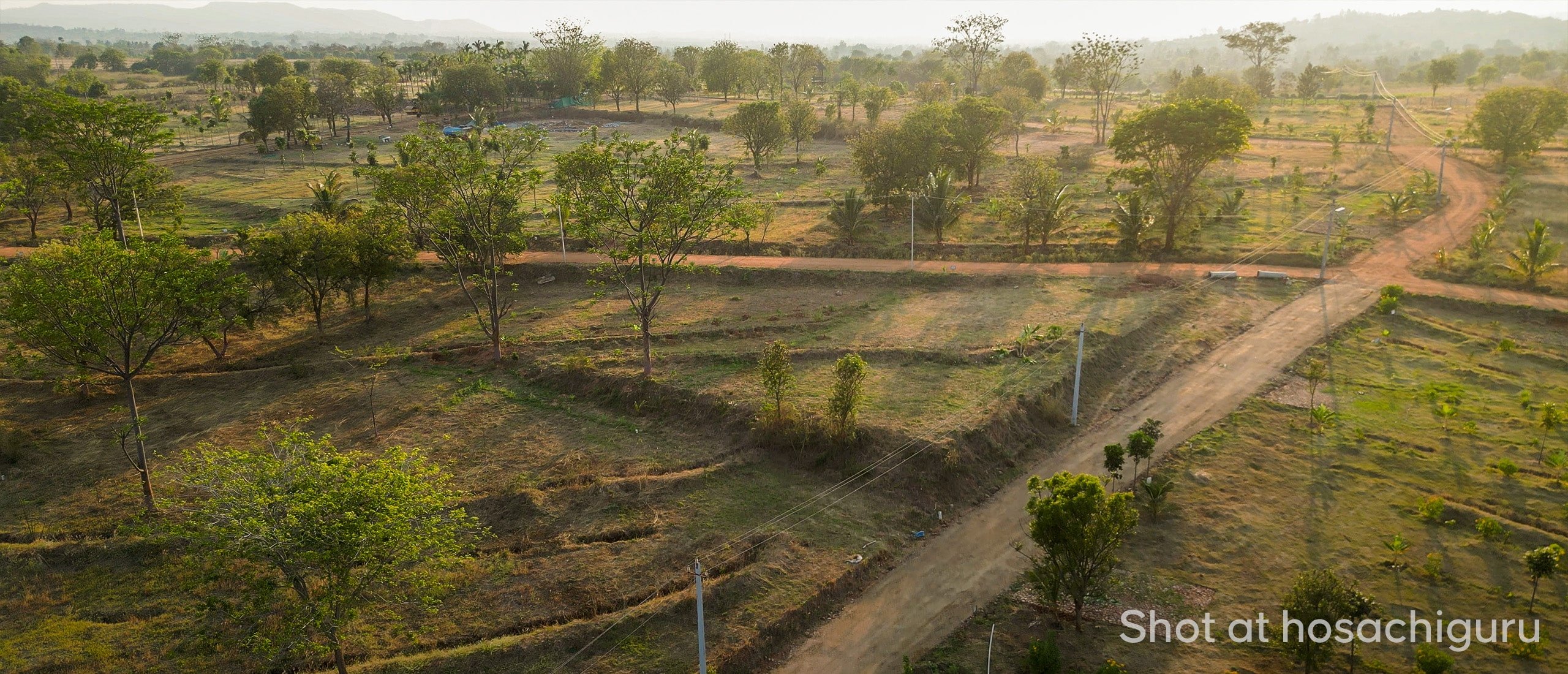
Hosachiguru’s efforts to Restore Wetlands at various Managed Farmlands
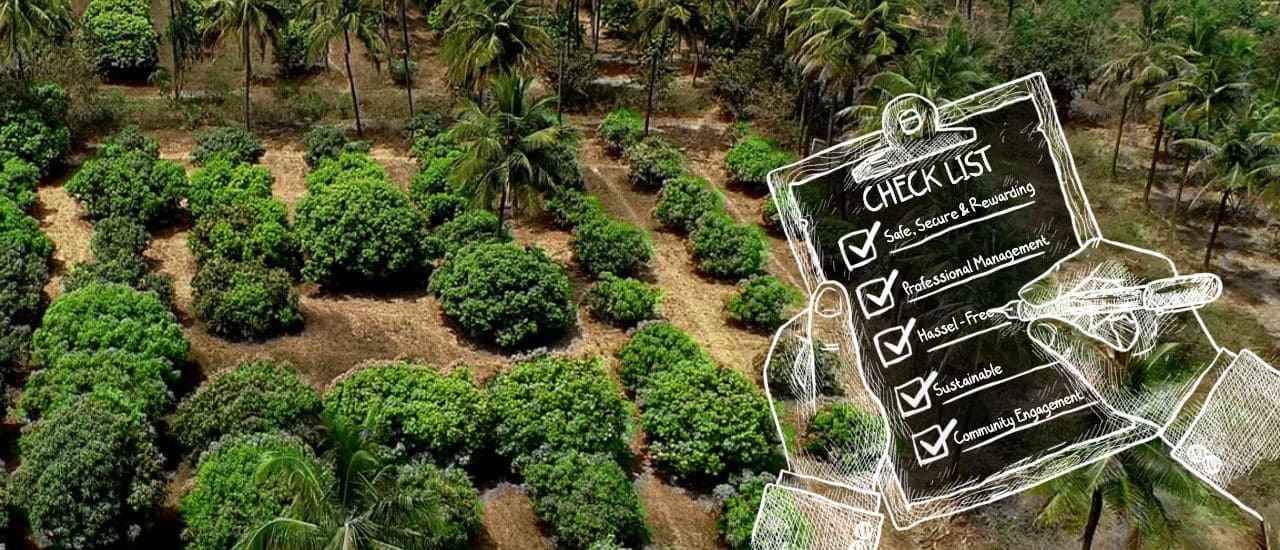
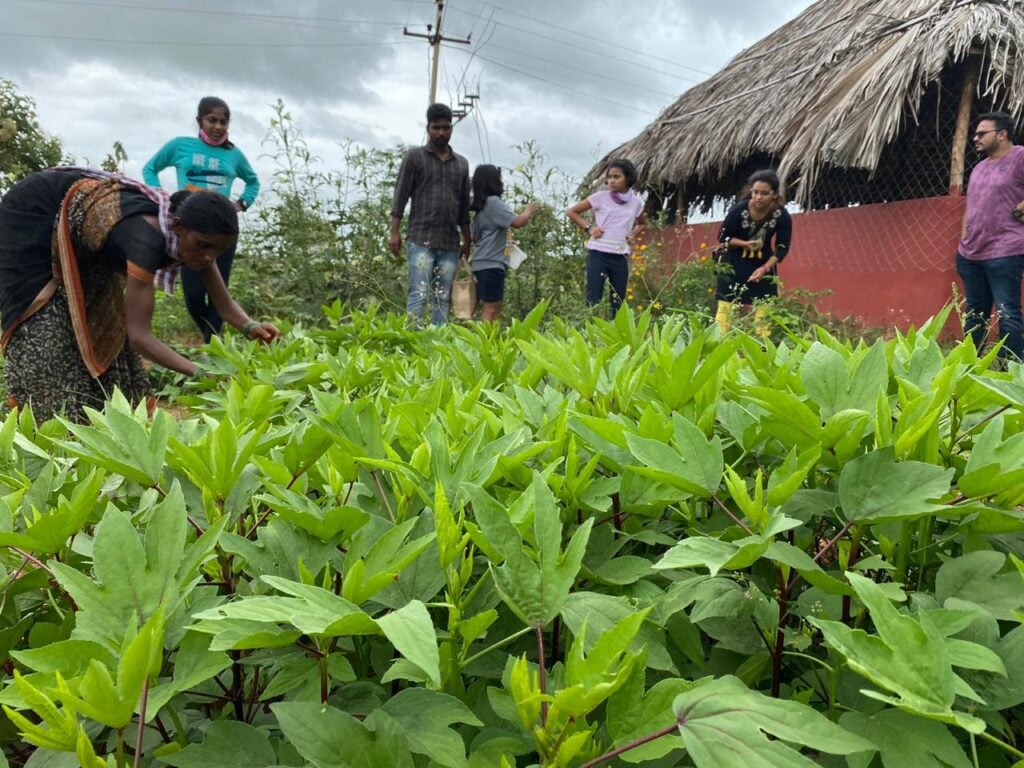
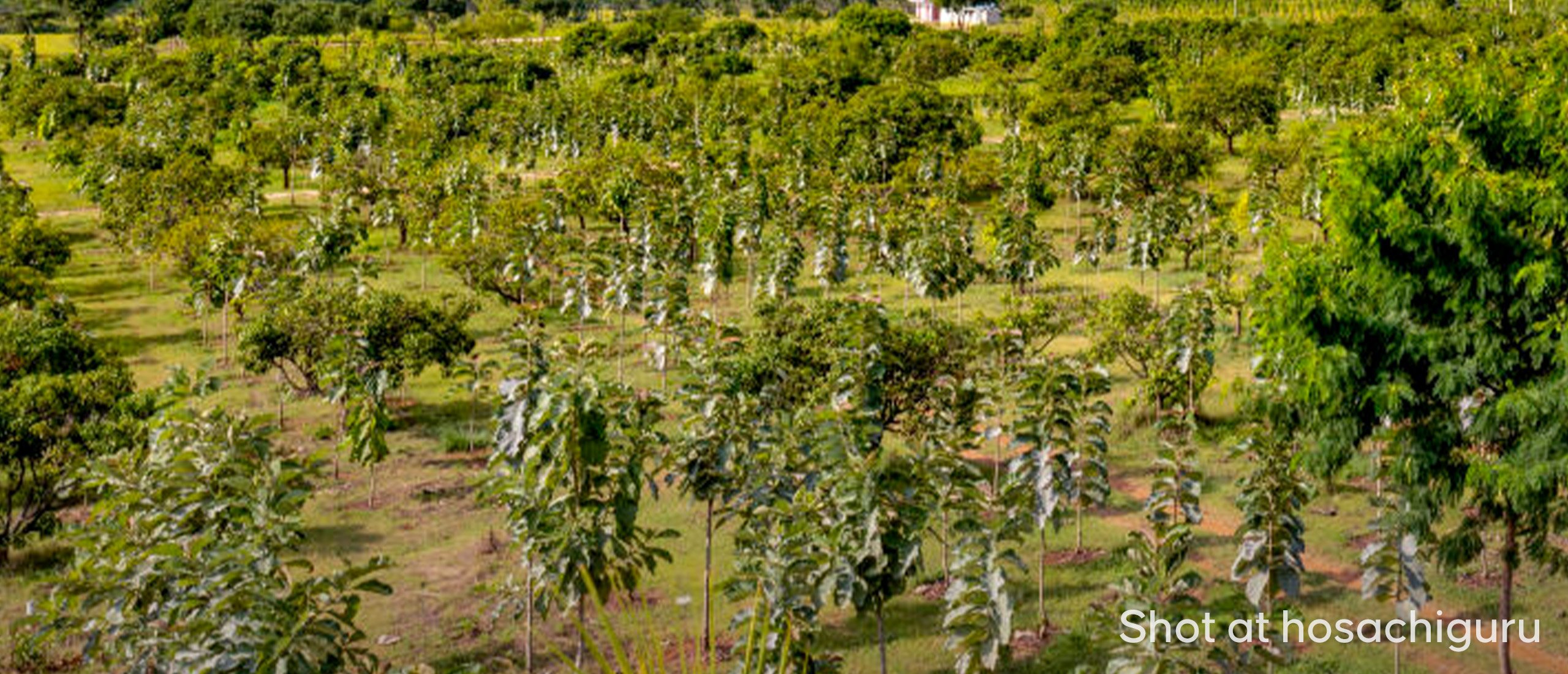
Permaculture principles are applied to achieve wetland restoration and conservation at various Hosachiguru Farms. The agronomy team at Hosachiguru identifies and maps the Wetlands. The team carefully evaluates the property based on location, size, and ecological significance. A wetland conservation plan is created and developed to protect and manage it. Activities such as reducing nutrient and pesticide runoff and avoiding drainage of wetland areas are executed. Degraded wetlands are restored by removing invasive species, re-grading or re-contouring the land, and planting native vegetation. Also, buffer zones are created for native vegetation around wetlands to filter pollutants and reduce erosion. A wetlands monitoring system is set in place to observe, identify and evaluate the effectiveness of the conservation efforts.
A connection is established between wetlands and other natural habitats to improve and enhance biodiversity to incubate and support a wide range of species. Also, the creation of diversified wetland habitats such as marshes, swamps, and bogs is executed. The use of swales, bioswales, diversion swales, permeable pavements, gully plugs, and other methods is executed to mimic the hydrology of wetlands. Lemon Grass, Vetiver, and Citronella are some of the native grass varieties that are planted to purify water. Riparian zones are created through the use of artificial structures such as sediment ponds and sediment basins, which are designed to trap sediment and pollutants before they reach wetlands.
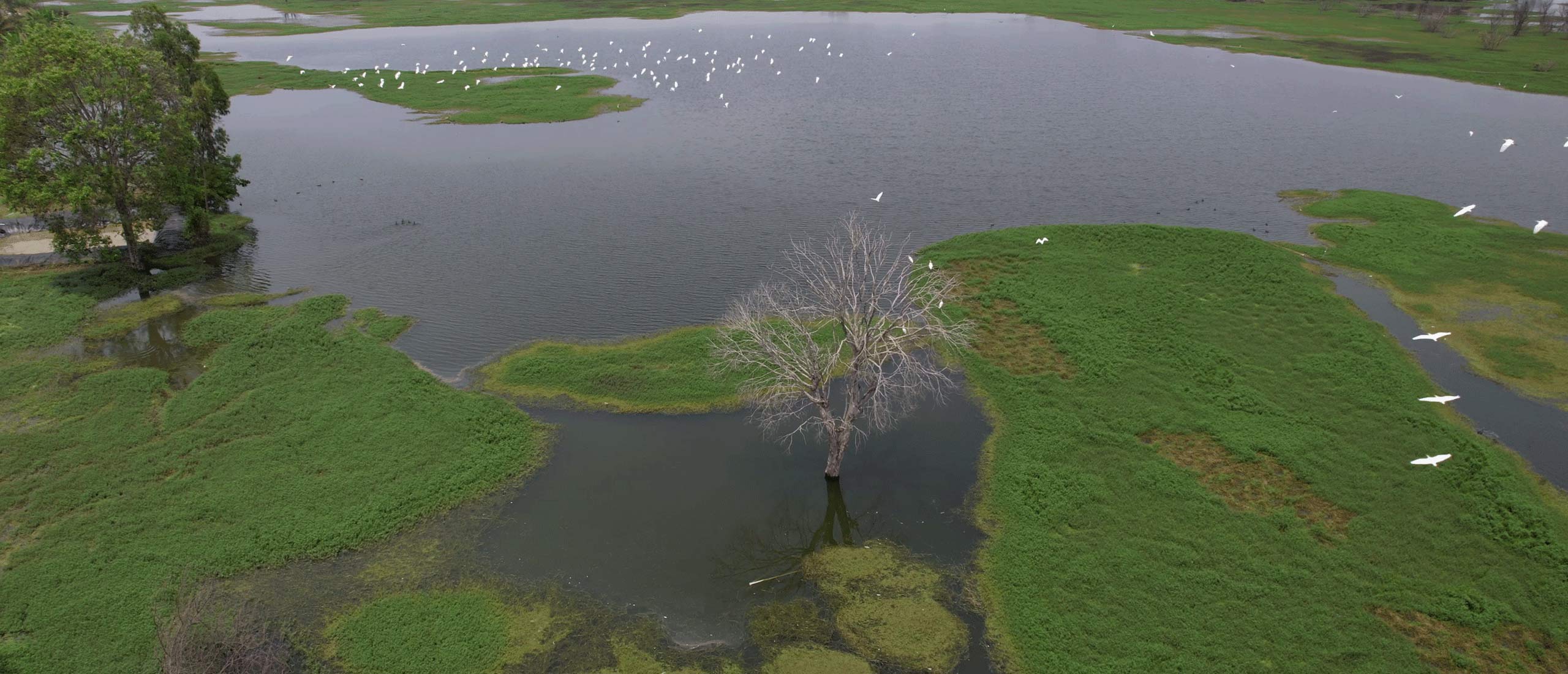
Areas adjacent to the streams and ponds are marked as Riparian zones at Madhuvana Farms by Hosachiguru. The vegetation in this area creates a unique wetland microclimate within a dry land ecosystem. It contributes to the land’s biodiversity and provides shelter to the native fauna. The vegetation also helps to stabilize the banks and stream beds in case of storm events and helps mitigate flash floods.
Agricultural systems are set up in such a way that it incorporates wetlands to provide benefits such as pollination, pest control, and soil fertility. The presence of water diversion trenches and stone bunds controls soil erosion. Aquatic plants such as Indian Lotus, Water Lily, water hyacinth, and water plantain facilitate pollination.
Hosachiguru follows the principles and practices of agroforestry, precision agriculture, and conservation farming to incorporate sustainable agricultural techniques that help to preserve wetlands and increase biodiversity.